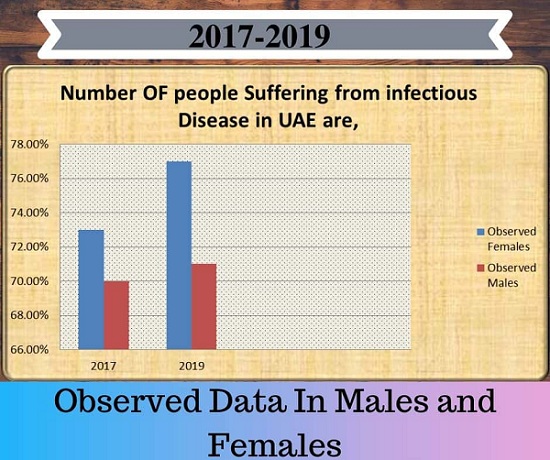
Theme: To Encourage Novel Discoveries in Therapeutics, Diagnostics and Vaccines for Parasitic & Infectious Diseases
Infectious Diseases Congress 2019
ME Conferences solicitations the participants from everywhere throughout the world to attend the “7th Annual Conference on Parasitology & Infectious Diseases” conference on November 14-15, 2019 to be held in Abu Dhabi,UAE which joins promote keynote shows, Oral talks, Poster presentations and Exhibitions. “To Encourage novel Discoveries in Therapeutics, Diagnostics and Vaccines for Parasitic & Infectious Diseases” is the main theme of the conference.
Parasitology specializes in inventive advancements which may hinder in unfold of and Infectious Diseases. This get-together incorporates exalting intelligent displays and keynote speakers UN organization can give a universal stage to talk of present and future challenges about Parasitology and Infectious Diseases.
ME Conferences sorts out 1000+ world Occasions exhaustive of 300+ conferences, 500+ anticipated and previous Symposiums and Workshops in USA, Europe and Asia with help from a thousand extra reliable social demands and passes on 900+ Open access Journals contains in significantly more than 30000 praised personalities, likely specialists as article board people.
Conference Highlights:
- Vector-Borne Diseases
- Emerging and Re-Emerging Infectious Diseases
- Aqua Culture Parasites and Risk of Human Health
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases and Infections of Reproductive Organs
- Paediatric Infectious Diseases
- Neglected Parasitic Infections (NPIS)
- Hospital Acquired Infections
- Agriculture and Veterinary Parasitology
- Medical Parasitology and Parasitic Infections
- Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Parasites
- Helminthology of Parasites
- Protozoan Parasites
- Arthropod Parasites and Ectoparasites
- Parasitic Diseases & Plant Parasitic Nematodes
- Pathology of Parasitic Infectious Diseases
- Parasitic Immunology
- Vaccines; Drug Development and Control Measures
- Laboratory Diagnosis - Therapeutic Parasitology
- Guidelines for the Prevention of Infectious Diseases
- Infection Control Practices and Health Care
- Anti-Microbial Chemotherapy
- Parasitic Ecology and Population Genetics
Target Audience:
- Microbiologists
- Bacteriologists
- Virologists
- Parasitologists
- Mycologists
- Pathologists
- Pharmacists
- Paediatrician
- Immunologists
- Epidemiologists
- Business Entrepreneurs
- Health Care Associations & Societies
- Research laboratories and academic institutes
- Manufacturing Medical Devices Companies
- Industry Research Scientists & CSO
- Directors of Associations and Societies
Track-1: Vector-Borne Diseases
In the study of disease transmission, a disease vector is an agent which carries and transmits an infectious pathogen into another living organism form to can a new infections; most of the agents which acts as vectors are creatures, such as intermediate Parasitic worms or organisms, however it could be a lifeless mode of contamination, such as dust particles. Mosquitoes, black flies, sandflies, ticks, and lice are compelling vectors of Infectious diseases, transmitting pathogens by means of their blood. Vector-borne diseases represent over 19% of every single irresistible disease, causing in excess of 600,000 passing’s were recorded annually. Among vector bore diseases are Mosquitoes borne and ticks borne diseases are rapidly spread and causes deathful diseases. They are the ailments caused by diseased viral vectors, parasitic vectors, etc. frequently found in tropical locales, where insects prevail, and access to drinking water and sanitation isn't protected.
Track-2: Emerging and Re-Emerging Infectious Diseases
Emerging Infectious diseases are caused by harmful pathogens are bacterial, fungal, viral infecting agents and protozoa which can spread by means of immediate or aberrant contact. Infectious diseases can be transmitted and from individual to another individual. Maladies can spread through the exchange of body fluids from sexual contact and during the blood transfusion. It is also conceivable to get an infection from an inanimate object which has recently been debased with a pathogen. Some infection-causing agents which live normally in the encompassing condition, however, can't be transmitted from individual to individual. Models of these pathogens incorporate Bacillus anthracis and histoplasmosis or blastomycosis. There are numerous new emerging infectious diseases which are ongoing devices accessible for the study of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), Herpes infection, Influenza virus infection, and a lot of more infectious diseases.
Track-3: Aqua Culture Parasites and Risk of Human Health
All fish carries pathogens and parasites. Like human and different other animals, fishes suffer from the marine effects of infection and parasites. Infection or disease is a prime agent influencing fish mortality, particularly when fish are young. Fish can constrain the effects of pathogens and parasites behavioral or biochemical means and such fish are consider under regenerative biology of fishes. Interfacing factors result in low-grade infection becoming fatal diseases. Fish safeguards against sickness are Specific and nonspecific. Non-specific defenses include skin and scales, and in addition, the bodily fluid layer discharged by the epidermis that traps microorganism and represses their development. If pathogens break these defenses, fish can create provocative reactions that expansion the stream of blood to contaminated territories and carry white platelets that endeavor to wreck the pathogens. Resistances are specific reactions to pathogens perceived by the fish's body, and its immune responses.
Track-4: Sexually Transmitted Diseases and Infections of Reproductive Organs
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are the infections which are passed from one individual then onto the next through sexual contact. Sexually transmitted diseases can be caused by microscopic organisms like bacterial, viral, fungal or parasites. Most STDs influence the men and women, but most of the medical issues they cause can be more serious for ladies. On the off chance that a pregnant lady has an STD, it can cause serious health issue for the child. Contingent upon the specific STD, some of the infectious diseases can spread by utilizing unsterilized medication needles, from mother to newborn child during childbirth or by breastfeeding, and blood transfusions. The genital areas are generally moist and warm conditions, and ideal for the growth of yeasts, fungal infections, and viral infections. Individuals can transmit microorganisms that possess the skin or mucous membrane of the genital parts. Some of the parasitic infectious diseases are AIDS, Hepatitis, Trichomoniasis, Gonorrhea, Herpes etc. Infectious organisms can likewise move between individuals in semen, vaginal secretions, or blood during sexual intercourse.
Track-5: Paediatric Infectious Diseases
Paediatrics is the field of medication that is concerned about the prosperity of neonatal, children, and adults. Pediatric infectious diseases are the ailments which will impact the child having a routine or persistence sickness or illness caused by infectious agents, for example, Bacteria, Fungus, viral infection and parasitic infections. The significant foundations for Paediatric Infectious diseases are fungal infections, parasitic disease, bacterial infections and viral contaminations. The global challenge of preventing malaria, Tuberculosis, and other rare infections which are caused during pregnancy. the Pediatric infectious ailments consolidate bone infections, skin infections, joint infection, blood defilements. In children has demonstrated that infectious diseases can be counteracted by getting to acquire proper awareness. The point of the study of Pediatrics is to decrease the infants and children death rate, control the spread of irresistible diseases, advance in healthy lifestyles of life for a long ailment free life and help opulence the problems of children and adolescents.
Track-6: Neglected Parasitic Infections (NPIS)
Neglected Parasitic infections are a worldwide health burden. Infectious diseases cause genuine ailments, including seizures, visual deficiency, cardiac diseases, and even demise. The effect of weakening illnesses caused by parasites is most prominent among the individuals who struggle to meet their day by day fundamental needs and access essential social insurance benefits in low-salary nations. Assessments of malady burden are regularly founded on serologic markers from cross-sectional populace ponders that demonstrate a person has been infected however not whether that individual has the dynamic disease. Proper and timely medical management of a person with an NPI is critical, however, the activities of Public health expected to distinguish and counteract tropical diseases and ailment tumble to the under-resourced and overburdened general public health issues. Targeted surveillance or screening programs in populaces are well on the way to be in danger could be an initial phase in enhancing trouble estimates, at moderately ease.
Track-7: Hospital Acquired Infections
An infection obtained in the health care units and hospitals by a patient who was conceded for a reason other than that disease or infections are also known as Nosocomial infections. The patient is exposed to an assortment of microorganisms during hospitalization. A disease happening in a patient in an emergency medical services or hospitals in whom the infections were absent or hatching at the season of incubating. This incorporates contaminations procured in the hospitalization yet showing after discharge, and occupational infections among the staff of the facility. Nosocomial diseases happen worldwide and influence both major causes of death and increased morbidity among hospitalized patients mostly bacterial diseases and fungal diseases. Hospital-acquired infections are among the real reasons for death and expanded among hospitalized patients. Medical centre obtained infections add to functional disability and emotional stress of patient and reduce the quality of life.
Track-8: Agriculture and Veterinary Parasitology
Veterinary parasitology is classified to consider the relationship between parasites and animals. Veterinary Infectious Diseases that can be normally transmitted between animals or even among creatures and human beings. Yet, contaminations are likewise influenced indirect way by parasites that reason infections in plants and animals that are nourishment for humans. Zoonoses can be caused by an extent of contaminating pathogens like infecting agents, microbes, viral agents and parasites. Veterinary diseases can be spread in different strategies for transmission, by zoonosis diseases or indirect zoonosis. Defilements may likewise cause in any setting in which there is tamed pets, savage or research contact with or usage of non-human animals, non-human creature items and subordinates. The most noteworthy zoonotic pathogens causing are food-borne pathogens, airborne, Vector-borne illnesses causing pathogens.
Track-9: Medical Parasitology and Parasitic Infections
Medical Parasitology is the study of parasites, and science that deals with a diverse symbiotic relationship between the host-pathogen interactions. Human beings are hosts to almost 300 types of parasitic worms and more than 70 types of protozoa, some derived from our primate progenitors and some procured from the creatures we have Domesticated or come in contact and cause different parasitic infections. Parasitology covers an extensive variety of themes which revolve around parasites, their taxonomic position, their structural and physiological science and pathogenicity. There are diverse branches for parasitology dependent on each predisposition, like research in Veterinary Science, medicinal, Structural, malariology, helminthology, parasite immunology.
Track-10: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Parasites
Parasitic nourishment is a method of heterotrophic sustenance where an organism lives on the body surface or inside the body of another sort of living being. The parasite gets nourishment from the body of the host. The parasites derive their nutrition from their host. This symbiotic interaction is regularly portrayed as harmful to the host. Parasites are depending on their host against the host defences for survival; were host provides nutrition and protection to the parasite. Because of this reliance, parasites have considerable adjustments to optimize parasitic nourishment and in this manner their survival. The biochemical molecules supplements which required from the host are amino acids, carbohydrates and lipids. Parasites are classified into two categories are endoparasites and ectoparasites. Parasites required supplements to complete fundamental capacities including reproduction and cell growth. The capacity of a parasite to import critical nutrients is central to its ability to be transmitted, to infect a host, and to cause disease and hence is an important component of pathogenesis.
Track-11: Helminthology of Parasites
Helminthology is the study of parasitic worms (helminths), while helminthiasis portrays the restorative state of being infected with helminths. Helminthology describes the scientific classification of helminths and their impacts on their hosts. Medical helminthology is concerned about the field of prescription that relates to helminths (worms) capable of diseases in individuals. These parasitic worms are responsible for the cause of disease all through the world and, although few types of helminthic parasites are perilous, their effect on human health is incalculable. Helminth parasitology has turned out to be one of the quick moving and interdisciplinary research regions over a spectrum of scientific activities from genomics, immunology and tropical medicines. With rapidly increasing sequence information, new medication advancement for treatment, and intricate host-parasite molecular interactions, research on these living beings and the maladies they cause is becoming ever more exciting and relevant to global health.
Track-12: Protozoan Parasites
A Protozoan parasite is fundamentally a protozoan that has adapted to invade and live in single cells and tissues of different life forms. There are a few protozoan parasites that reason issues and few protozoans are infected with the virus. Parasitic protozoan diseases represent a major health burden in the creating a scene and contribute fundamentally to the dreariness of neonatal mortality. They are available in our sustenance, soil and water which can make us exceptionally wiped out on the off chance that they ever sneak inside us. Each unique protozoan parasite can cause an alternate infection or sickness in our bodies. Some can cause serious diseases of the lower respiratory infections, and the central nerves system. while others live in our digestive system and cause side effects like diarrhoea and are not deadly. Malaria fever is a sign of the protozoan parasites that infect man. Mostly protozoan parasite infections like malaria, babesiosis, trichomoniasis, etc. are found in tropical regions of the world.
Track-13: Arthropod Parasites and Ectoparasites
Arthropods form is a major group of pathogen vectors with mosquitoes, flies, sand flies, lice, insects, ticks, and bugs transmitting in a countless number of pathogens most of them are viral vectors. Ectoparasitic infection is a parasitic ailment caused by organisms that live principally on the surface of the host. Arthropods imperative in causing vector-borne diseases, however, are much more essential as vectors, or transmitters, of a wide range of pathogens that thus cause enormous grimness and mortality from the diseases they cause. There are three principal classes of parasites that can cause diseases in humans are: protozoa, helminths, and ectoparasites. Arboviral illness is a general term used to portray infections caused by a group of viruses which spread to individuals by the bite of tainted arthropods, insects such as mosquitoes and ticks.
Track-14: Parasitic Diseases & Plant Parasitic Nematodes
Parasites are the organism that inhabits off different another living organism, or hosts, to endure. A few parasites don't discernibly influence their hosts. Others develop, reproduce, or attack organ system that makes their hosts diseased, bringing about a parasitic disease or infectious diseases. epidemiology of plant diseases which causes parasitic diseases are also a major issue in tropical and subtropical districts of the world. Plant disease is also one of the deadliest parasitic diseases. The symptoms of parasitic infections vary depending on the organism and may not always be obvious. There are no vaccines for most of the parasitic diseases, but Some medicines are available to treat parasitic infections. There are no vaccines for parasitic diseases. Some medicines are available to treat parasitic infections. Most diseases are caused by multiple processes, Plants are one of the major sources of allergens which elicit an allergenic response by immunoglobulin E (IgE) mediated allergies. Population genetics of plant pathogens are related (PR) to large instigated by different sorts of pathogens, for example, microorganism like bacterial, viral, fungal pathogens, and parasites.
Track-15: Pathology of Parasitic Infectious Diseases
Parasite pathology can have an extensive variety of pathophysiological impacts on the host. A parasitic diseases, otherwise called parasitosis, is an irresistible infection caused or transmitted by a parasite Many parasites don't cause sicknesses as it might in the end prompt demise of both life form and host. Parasitic infections can influence for all intents and purposes every single living being, including plants and warm-blooded animals. Parasitic contaminations can typically be treated with antiparasitic drugs. For some parasitic sicknesses, there is no treatment, and, on account of genuine side effects, medical trails or drug medical trails are also expected to execute the parasite is managed, though, in different cases, side effect alleviation alternatives are utilizing. Pathology includes seeing tissue tests with the end goal to analyze an infection.
Track-16: Parasitic Immunology
Immune response being the defence centre of our body provides immunity which is termed as the process in which our body defends itself against a foreign particle. Parasitic immunology is based on how hosts control parasites and the immunopathological reactions which take place in the course of parasitic infections. Immunology is a large therapy area characterized by maladies of the immune system, specifically an aberrant immune response against healthy tissues present in the body, leading to chronic or acute inflammation. Parasitic Immunology is an integral of other branches and each branch is interdependent. Depending on the specific site affected or effect of the parasite, this can lead to various types of chronic pain and loss of mobility and have a negative impact on quality of life. Immunopathology is a branch of biomedical science stressed over safe responses to an ailment, with immunodeficiency diseases, and with infections which caused by resistant instruments. It joins the study of the pathology of a living being, organ structure, or disease regarding the immune system.
Track-17: Vaccines; Drug Development and Control Measures
Presently disease control and treatment of parasitic infections are focuses on parasitic and viral infections chemotherapy, but re-infection often happens without continued treatment, creation vaccination a far desirable option as a simple, one-step procedure to interrupt transmission. Many improvements are underway in the field of genomics in infectious diseases, as well as novel technologies have been introduced for vaccine delivery systems. Most of the vector-borne diseases are a revolutionary, ignored, however common cause of death throughout the world. It causes over 13% deaths per year. However, there are certain steps and standard guidelines are can be occupied to control its. Endemicity of some infectious diseases like malaria endemicity whose frequency are declining, due to prevention exertions and scientific advances in treatment and vaccines, malaria occurrence continues to rise due to widespread resistance to many of the present drugs. There are no successful malaria vaccines. Antiparasitic drugs have been utilized effectively to control parasitic ailments in creatures for a long time, as they are protected, cheap and successful against an expansive range of parasites. Novel vaccination and antibiotics are also prepared based on the infecting agent mechanism, growth and mode of transmission.
Track-18: Laboratory Diagnosis - Therapeutic Parasitology
Techniques for the determination of infectious diseases have stagnated in the last 20– 30 years. Barely major advances in clinical indicative testing have been made since the presentation of PCR, although new advanced technologies are being explored. Many tests that form the backbone of the clinical microbiology are based on very old and labour-intensive technologies. Ongoing advancements in new symptomatic devices, be that as it may, reliable immense enhancement in parasite recognition. The viable control and treatment of parasitic diseases require rapid, dependable, Specific tests which can also serve to screen the adequacy of the therapeutic and prophylactic protocol. Parasitic infectious diseases are generally determined to have tests of faeces, urine, blood and tissue. Pathology diagnosis of parasitic infectious diseases requires highly sensitive and specific tests. In many cases, the identification of parasites concerns the study of the transmission of infectious diseases and it is vital to recognize species and subspecies.
Track-19: Guidelines for the Prevention of Infectious Diseases
When typical signs and symptoms of some commonly encountered communicable diseases are noticed care should be taken. Some of the communicable diseases have more than one mode of transmissions and infection control guidelines are followed to reduce infectious diseases. General guidelines on the management of suspected outbreaks of Infectious diseases- Tropical medicines and hygiene, Environmental Cleaning/Disinfection, Isolation Precautions, Injection Safety, Antimicrobial Stewardship, Healthcare Personnel. The aseptic method is a key part of all invasive medical strategies. So also, disease control measures are best when Standard Precautions (medicinal services) and Community health are applied because undiagnosed contamination is common. In cases where infections are just suspected, an individual might be isolated until the point that the incubation period has passed, and the diseases show itself or the individual remains healthy.
Track-20: Infection Control Practices and Health Care
Infection prevention or counteractive action and control is required to keep the transmission of transmittable diseases in all human care services settings. Infection control precautions are an arrangement of standard suggestions used to diminish the risk of transmission of infections causing agents from body fluids or natural surfaces that contain infecting agents and treatment for Infectious Diseases. Selected patients may require safety measures to restrain the transmission of potential infecting agents to different patients. Recommended isolation precautions depend on the course of transmission are Droplet, Airborne and water-borne diseases, and Infection by direct or indirect contact.
Track-21: Anti-Microbial Chemotherapy
Antimicrobial drug development is the clinical use of antimicrobial agents to treat infectious diseases caused by the effect of microorganism and other infecting agents. Obstruction may include reducing the effect of the medication, changes in the receptor of the medication, or metabolic inactivation of the medication impacts antimicrobial chemotherapy. A Combinations of anti-infection agents may act synergistically-creating an impact more effect than the whole of the impacts of the two medications alone or inimically if one operator hinders the impact of the other. Antimicrobials can be classified by at least three different schemes are Effects on cells, Range of activity, and Sites of activity. Antimicrobial agents encompass both synthetic compounds and natural products or antibiotics. Most of the antimicrobial drugs synthesized or isolated do not possess the requisite selectivity to be useful in the treatment of infectious diseases that is, they affect the host organisms as well as the parasites.
Track-22: Parasitic Ecology and Population Genetics
Parasites can function as both in the form of predators and prey. Parasites which feed on hosts nutrition in a special type of predation for the survival. Parasitism and parasite evolution was a major aspect of evolutionary environmental science. Even though parasite-host interactions were plainly ecological and important in evolution, Parasite-host interaction is necessarily co-distributed species with the distribution of parasites overlapping that of their specific habitat (the hosts). This is even more constrained if the set of host species is limited for a given parasite species and the host-parasite population genetics and evolution are known as coevolution. host-parasite studies may help predict the potential for local adaptation by determining the relative dispersal rate between a host and its parasite. Based on the comparison of the phylogeographical histories, population genetics, population structures and population divergence times of three co-distributed and phylogenetically independent ectoparasitic and endoparasites organism insect species.
Theme: To Encourage Novel Discoveries in Therapeutics, Diagnostics and Vaccines for Parasitic & Infectious Diseases
Summary:
Infections are the activity of living being on body tissues by Infection causing agents, their augmentation, and conjointly the response of host tissues to the irresistible disease-causing agents and the toxins they demonstrate. Infection-causing agents like viroid's, prions, microbes, nematodes arthropods, mycosis, and completely unique parasites creatures of different helminths. Parasitology is that the science adapting to parasites that contaminate man, delivering sickness and hopelessness in many nations of the tropics. The conclusion of parasitic infections relies upon numerous lab procedures, imaging techniques, and scrutiny also to clinical picture and geographic area. Parasitic illnesses could likewise be presented by a decent type of clinical indications steady with the tissue invaded. Consequently, there's a craving for the coordination between established researchers to make sense of a long and pass on the novel drug.
Importance & Scope:
Infectious Disease Congress 2019 is an excellent and open platform to gain information and to explore in the field of bioscience. It is captivating to request that all of you visit and enlist for "7th Annual Conference on Parasitology and Infectious Diseases" planned for Gregorian timetable month of November 14-15, 2019 Abu Dhabi, UAE.
This conference conduct alongside professors, researchers, scientists, students altogether the areas of medical sciences, pharmaceutical, Life sciences, Medical associations, and societies, permits a global forum to explore the approved analysis. Parasitology and infectious diseases conference can give a platform for all the participants to debate regarding the exciting advances that hold promise in reducing parasitic diseases, promising breakthroughs within the development of vaccines against medically vital parasites and additionally regarding the technological and abstract advances within the field. All members of the Infectious diseases 2018 organizing committee foresee to meeting you in Johannesburg, South Africa.
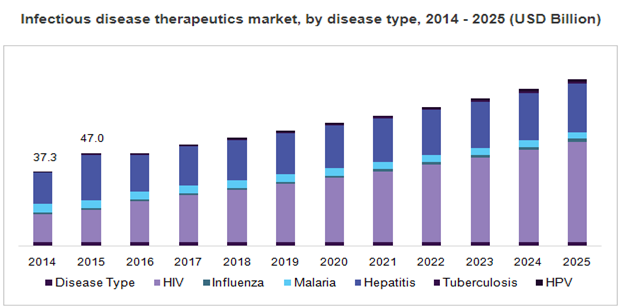
Global Market Research on Infectious Diseases:
The global infectious disease medicine market size was valued at USD 56.88 billion in 2016 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.6% throughout the forecast amount. the worldwide marketplace for infectious diseases is growing at a gradual pace since the past few years. the worldwide infectious diseases market is expected to expand at a CAGR 8.0% over an eight-year forecast amount, in 2018-2024.
The revenues are expected to achieve US $ 1503.8 Mn by the top of 2024. additionally, the market is probably going to witness the patent expiration of the many medications throughout the forecast amount. However, lack of awareness regarding treatments for these disorders and low adoption of treatments are the factors which expected to restraint the expansion within the coming back years.
Why Abu Dhabi?
Most of the Abu Dhabi conferences achieve success with flying colors are associated with a broad vision of higher future for property development and in the analysis of conference in Abu Dhabi, 2019 is being proclaimed with an expectation of a redoubled range and development of profession to come back and facilitate building the long run.
In “developing” nations such as Abu Dhabi, social epidemiology is cast in a new light owing to these countries’.
Abu Dhabi is portrayed by the great infectious diseases burden and, overall, the weakest general public foundation among all regions in the world. Habitually, vertically situated diseases surveillance programs at the national dimension or more in Africa regularly result in an excess of paperwork’s, such many various directions, diverse wordings, too many administrators, and conflicting priorities.
Abu Dhabi is to distinguish a gathering of need diseases are classified as pandemic inclined infections, diseases focused for reduction or complete elimination, and different maladies of public health significance. The challenge will be to coordinate surveillance and epidemic preparedness and response activities for these need illnesses, particularly when there are weakened ministries of health.
Hospitals:
Major Infection Prevention Hospitals in the World
- Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC)
- Monroe Carell, Jr. Children's Hospital at Vanderbilt
- Nashville Veterans Affairs Medical Center (VA)
- Denver Public Health, Infectious Diseases Clinic
- Jackson Memorial Hospital
- Arnold Palmer Hospital, HUG-Me Program
- The CORE Center of Chicago
- Johns Hopkins Hospital
- Tufts-New England Medical Center
Major Infection Prevention Hospitals in Abu Dhabi
- Oasis Hospital
- Medeor Hospital
- Canandian Specialist hospital
- Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi
- Avivo Hospital
- Alsalma Hospital
- Tawam Hospital
- Iranian Hospital
- Burjeel Hospital
- NMC Speciality Hospital
- Mediclinic Hospital
Associations and Societies:
Major Infection Prevention Research Associations around the Globe
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control
- Infection Prevention Society
- British Infection Association
- Infectious Disease Society of America
- European Society for Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases
- British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy
- Society for General Microbiology
- British HIV Association
- The Society of Healthcare Epidemiology of America
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- Asia Pacific Society of Infection Control
- Infection Prevention & Control - American Nurses Association
- Infection prevention and Control Canada
- The Infection Control Nurses Association
- Infection Control - California Hospital Association
- Infection Control Association of Zimbabwe
- International Federation of Infection Control
- Texas Society of Infection Control & Prevention
- Philippine Hospital Infection Control Society
- Infection Control Association of NSW
Major Infection Prevention Research Associations around Abu Dhabi
- Khalifa University
- Department Of Health-Abu Dhabi
- SEHA Abu Dhabi
- American Society Of Parasitologist
- Abu Dhabi Research Ethics Committee
- Dubai Harward Foundation For Medical Research
- Al Jalila Foundation
- Clinical Research Organization
- Emirates Medical Association
- Dubai Health Authority
Medical Universities:
Major Infection diseases related to Universities in the World
- University of Cambridge
- Kings College of London
- London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine
- Imperial College London
- UCL Institute of Epidemiology and Healthcare
- University of Sheffield
- Paediatric Infectious Diseases Society
- Columbia University
- University of Maryland
- Swedish Institute for Infectious Disease Control
- Uppsala University
- University of Gothenburg
- University of Otago
- Oslo University
- University of Pittsburgh
- Emory Health Sciences
- Queensland University of Technology
- University of Liverpool
- University of Colorado Denver
- Infectious Diseases Society of America
- Medical College of Georgia at Georgia Regents University
Top Infection diseases related to Universities in Abu Dhabi
- Khalifa University
- Abu Dhabi University
- Zayed University
- United Arab Emirates University
- Masdar University Of Science And Technology
- University Of Sharjah
- Ajman University
- American University Of Sharjah
- Al Ain University Of Science And Technology
- Gulf Medical University
- Canadian University Dubai
Companies Related to Parasitic Infectious Diseases:
List of publicly trading healthcare companies
- Abbott Labs
- Allergan
- Amgen
- Biogen
- CVS Health
- Eli Lilly
- Henry Schein
- Merck
- Regeneron Pharm
Infectious Disease Industry
- Achillion Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (ACHN)
- Emergent Biosolutions, Inc. (EBS)
- Melinta Therapeutics, Inc. (MLNT)
- Sarepta Therapeutics, Inc. (SRPT)
- Chembio Diagnostics, Inc. (CEMI)
- Genocea Biosciences, Inc. (GNCA)
- Vical Incorporated (VICL)
- Aethlon Medical, Inc. (AMED)
- Dynavax Technologies Corporation (DVAX)
- BioCryst Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (BCRX)
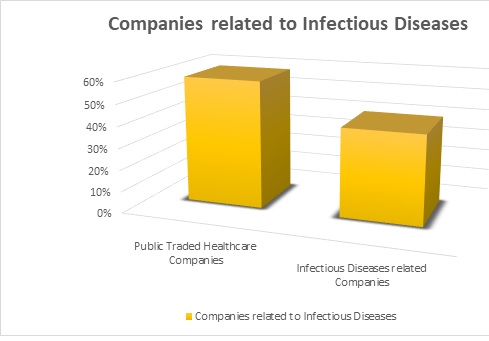
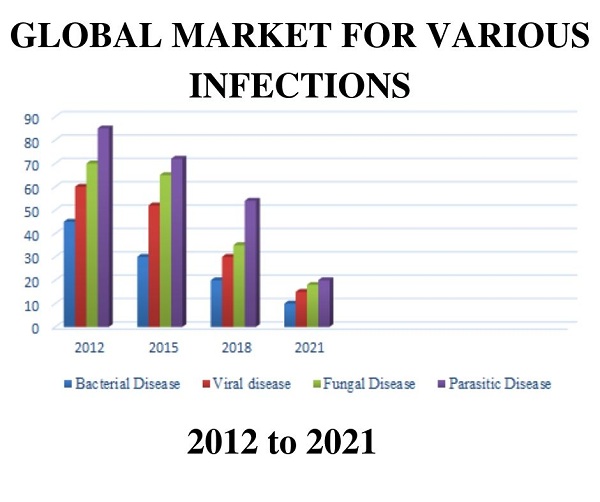
A glance at Market for Infectious Diseases Research
The communicable disease epidemics are exploding worldwide, raising an in-depth demand for diagnostic tests. Moreover, the incidences of protozoal infection, flu, AIDS, and alternative diseases are rising, making a strong demand for communicable disease. By the top of 2016, this section is calculable to account for over 28% share of the market revenues.
Based on the regional analysis, the worldwide Infectious disease market is divided into 5 key regions, North America (the U.S. and Canada), Latin America (Brazil, Mexico, and remainder of Latin America), Europe (France, Germany, Italy, Spain, the U.K., Russia, and remainder of Europe), Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, Australia, New Sjaelland, ASEAN, and remainder of APAC), and Middle East (GCC countries, African country, and remainder of MEA). APAC and ME are predicted to stay the foremost markets throughout the forecast amount.
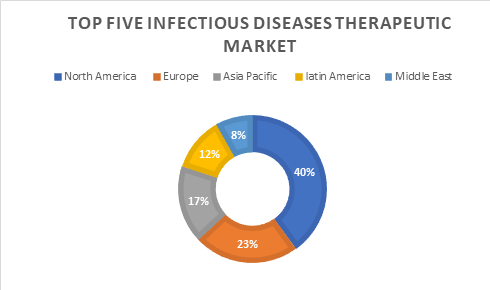
While governments of assorted countries in the Asia Pacific are more and more registering higher demand for infectious diseases diagnostic kits leading to the biggest market during this region, the ME market will witness a considerably growing market thanks to growing governmental initiatives.
Related Conferences:
- Australasian Viral Hepatitis Elimination Conference 2019; August 5 - 6 2019 Novotel Sydney Brighton Beach
- 12th Global Infections Conference;September 09-10, 2019 Singapore
- 14th World Congress on Inflammation; September 15-19 ,2019 Sydney
- World Congress on Infection Prevention and Control; September 18-19, 2019 Edinburgh, Scotland
- 6th International Conference on Mycology and Fungal Infections; October 07-08, 2019 Madrid, Spain
- “3rd International Conference on Worldwide Infectious Diseases” ; October 21-22, 2019, London, United Kingdom
- 2nd International Conference on Antimicrobial and Antibacterial Agents; November 11-12, 2019 Istanbul, Turkey
- World Conference on Vaccine and Immunology ; November 22-23, 2019 Dubai, UAE
- Infectious Diseases Conference; December 04-05, 2019 New York, USA
- 13th Edition of International Conference on Infectious Diseases;April 13-14, 2020 London,UK
Related Associations:
USA: Infectious Disease Society of America; Infectious Diseases Research Network; Canadian Society for Immunology; Society for General Microbiology; Canadian Association for Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases; National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases; Canadian Public Health Association; Tropical Pathology & Infectious Diseases Associations; International Society for Infectious Diseases; Michigan Infectious Disease Society; Texas Infectious Disease Society; Infectious Disease Association of California; International Antiviral Society; American Society for Microbiology; Infectious Disease Society of New Jersey; Australasian Society for Immunology Inc; Canadian Association for HIV Research; The Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists; Infectious Disease Society of Ohio
Asia-Pacific & Middle East: Clinical Infectious Diseases Society; Japan Society for Surgical Infection; Victorian Infection & Immunity Network; Australasian Society for Infectious Diseases; Victorian Infection Control Association; Victorian Infection Control Professionals Association; Infection Control Practitioners Association of Queensland; Infection Control Association of South Australia; Infection Control Association of Western Australia; Hospital Infection Society; Clinical Infectious Diseases Society; Japan Society for Surgical Infection; Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases; Australasian Society for Infectious Diseases; Asian Society for Pediatric Infectious Disease; Infectious Diseases Society of Taiwan; Pediatric Infectious Disease Society of Thailand; Australian Society for Antimicrobials; Chinese Society for Immunology; Pediatric Infectious Disease Society of the Philippine; Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases; Japanese Society for Medical Mycology; Korean Society of Pediatric Infectious Diseases; Japanese Society for Bacteriology
Europe: Spanish Society of Paediatric Infectious Diseases; Spanish Society of Paediatric Clinical immunology and Allergy; Spanish Association of Paediatric Primary Care; Federation of Infectious Diseases Societies of Southern Africa; British Society for Immunology; European AIDS Clinical Society; European Society for Immunodeficiencies; Scandinavian Society for Immunology; National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases; European Society for Infection in Urology; European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases; Italian Society of Infectious and Tropical Diseases; Austrian Society for Infection Control; Swiss Society for Infectious Diseases; Swiss Society for Microbiology; Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology Specialty Society of Turkey; Turkish Society of Clinical Microbiology; Turkish Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases; Turkish Society of Microbiology; British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy; Infection Prevention Society; European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases
Conference Highlights
- Vector-Borne Diseases
- Emerging and Re-Emerging Infectious Diseases
- Aqua Culture Parasites and Risk of Human Health
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases and Infections of Reproductive Organs
- Paediatric Infectious Diseases
- Neglected Parasitic Infections (NPIS)
- Hospital Acquired Infections
- Agriculture and Veterinary Parasitology
- Medical Parasitology and Parasitic Infections
- Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Parasites
- Helminthology of Parasites
- Protozoan Parasites
- Arthropod Parasites and Ectoparasites
- Parasitic Diseases & Plant Parasitic Nematodes
- Pathology of Parasitic Infectious Diseases
- Parasitic Immunology
- Vaccines; Drug Development and Control Measures
- Laboratory Diagnosis - Therapeutic Parasitology
- Guidelines for the Prevention of Infectious Diseases
- Infection Control Practices and Health Care
- Anti-Microbial Chemotherapy
- Parasitic Ecology and Population Genetics
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | November 14-15, 2019 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Bacteriology & Parasitology Open Access
- Mycobacterial Diseases
- Journal of Infectious Diseases & Therapy Open Access
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by